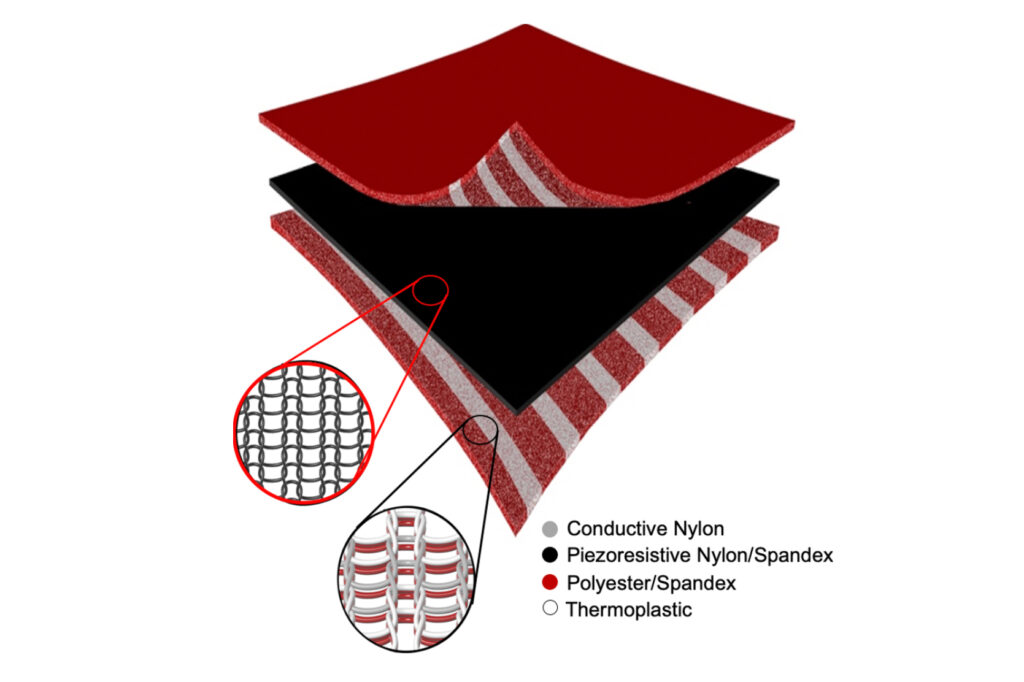
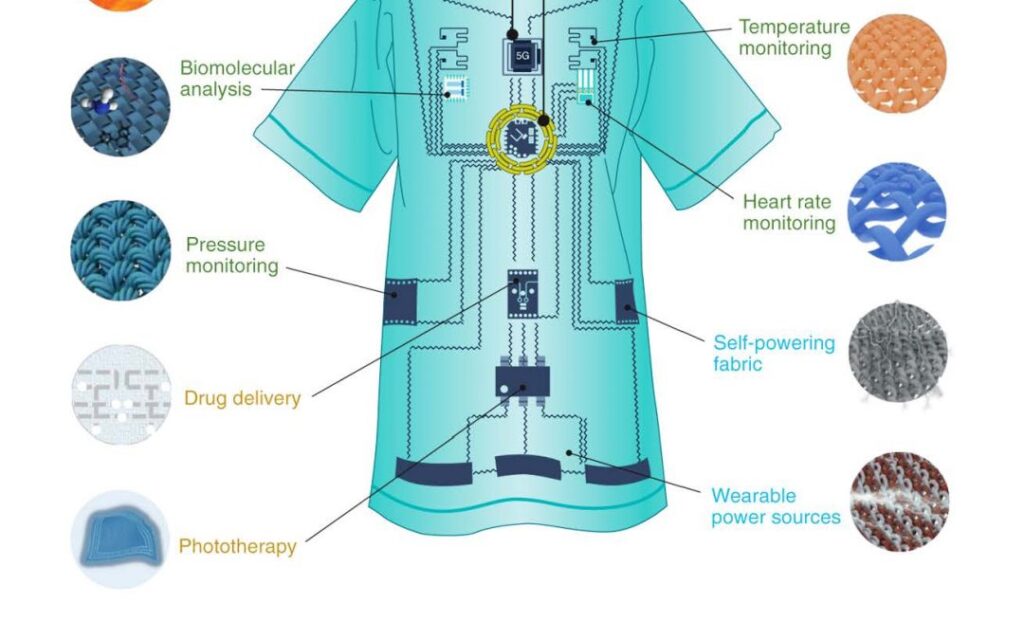
Technology & Innovation in Textiles
The textile industry is undergoing a radical transformation thanks to emerging technology and innovation in textile that blend design, engineering, and sustainability. From smart fabrics that monitor our health to custom-fit garments printed in 3D, innovation is challenging traditional production and unlocking new creative frontiers. To learn more and shop more visit this site. This post explores four ground-breaking domains reshaping textiles in 2025 and beyond:
- Smart & E‑Textiles
- 3D‑Printed & 4D‑Responsive Textiles
- Sustainable and Biodegradable Electronics
- Solar & Energy‑Harvesting Textiles
1. Smart & E‑Textiles
Smart textiles—fabrics integrated with electronic sensors—have progressed from sci-fi concepts to real-world products in healthcare, sports, and wellness.
👕 Full-Body Sensor Networks
Innovative research by Ryo Takahashi and colleagues is pushing boundaries with digitally-knitted, battery-free NFC sensor garments, enabling body-wide health monitoring through conductive yarns and meander coil design. These systems deliver efficient data and power transfer without bulky batteries
👩⚕️ Health Monitoring & Fitness
3D microfiber-based electrode textiles, engineered for conformability and low impedance, allow real-time ECG and EMG monitoring—even underwater or during maternal health sessions
🏃♂️ Consumer Smartwear
Commercial smart shirts like Hexoskin embed heart rate and respiratory sensors into everyday garments, making real-time biometric tracking accessible for athletes and health researchers
📌 Takeaway: Smart textiles are becoming more user-friendly and power-efficient. As knitting and weaving tech improves, expect garments that seamlessly track health and environment.
2. 3D‑Printed & 4D‑Responsive Textiles
🎨 Creative Freedom & Sustainability
3D printing minimizes material waste by using only essential amounts, enabling eco-friendly, on‑demand production. A European Commission study found it could save up to 90% of raw materials . Hybrid techniques like FDM, SLS, and PolyJet (e.g., Stratasys J55 Prime) are creating diverse, vibrant fabrics directly from CAD models .
👟 Footwear Revolution
Innovative soles are being 3D‑printed using TPU and TPE for flexibility and durability. For instance, NIFT Gandhinagar students showcased custom midsoles/insoles for everyday runners . Globally, disruptive startups like Zellerfeld are producing personalized shoes from aggregated athlete data—even while big brands scale slowly . Adidas’ Futurecraft 4D, Nike’s Flyprint, and Reebok’s Liquid Factory harness this for performance-driven customization .
👗 Couture & Avant‑Garde
Designers like Iris van Herpen and Danit Peleg are pioneering wearables with sculptural complexity. Van Herpen’s 3D-printed wedding dress and Peleg’s printed jacket collections have demonstrated both artistry and feasibility.
🔄 Emerging 4D Textiles
4D printing introduces materials that change over time—responding to heat, moisture, or light. Textile markets leveraging this tech continue growing (CAGR ~42%) and are set to impact sectors like aerospace and healthcare soon .
📌 Takeaway: 3D printing blends sustainability, personalization, and design innovation. From footwear to fashion-forward wearables, it’s dismantling linear production and empowering designers.
3. Biodegradable Electronics & Eco‑Friendly E‑Textiles
Electronic components in textiles pose waste challenges. But regenerative tech is emerging:
- Projects like UWE’s SWEET use biodegradable conductive materials (graphene, PEDOT:PSS) to create compostable EKG and temperature-sensing textile devices .
- Cornell’s Eco-Threads illustrate undergarments and picnic blankets with biodegradable sensors that naturally degrade by ~50% in four months .
📌 Takeaway: Biodegradable electronics can drastically reduce e-waste. As sustainable materials advance, we may soon wear tech that disappears safely instead of polluting landfills.
4. Solar & Energy‑Harvesting Textiles
Power-on-the-go? Textiles are gaining energy-generating features:
- Solar cell fabrics embed PV fibers or coatings into textiles, offering flexible, lightweight generation—ideal for backpacks, jackets, or tents
- MIT and Johns Hopkins labs are advancing battery-integrated solar fibers, merging energy harvesting and storage into wearable fabrics.
📌 Takeaway: Solar textiles are moving beyond prototypes to practical products, potentially powering wearables and gadgets from clothing itself.
🧭 Challenges & The Road Ahead
| Challenge | Status & Outlook |
|---|---|
| Scalability & Cost | 3D printing remains costly for mass production; economies of scale ongoing . |
| Durability & Comfort | E-textiles must balance comfort with conductive longevity. Waterproofing, flexible substrates, and better yarn tech are advancing. |
| Regulatory & Privacy | Health-tracking textiles introduce data security concerns—necessitating standards and encryption. |
| Consumer Adoption | Smartwear’s comfort, usability, and price must improve for mainstream acceptance. |
- Customization on Demand: Consumers will soon enjoy made-to-measure garments and shoes—reducing waste and overstock.
- Wellness Integration: Regular clothing might include built-in health sensors, alerting wearers to anomalies before they become serious.
- Circular & Regenerative: Biodegradable electronics and recyclable materials will pave the way for textile products that can be returned, repurposed, or safely composted.
- Art Meets Engineering: Designers and engineers will collaborate to create pieces that are not only functional but sculptural and personalized—transforming fashion into kinetic art.
✍️ Conclusion
In 2025, Technology & Innovation in textiles are more than just fabrics—they’re platforms where Innovation, Sustainability, Function, and Style converge. From smart garments that monitor our physiology, to 3D-printed shoes and biodegradable sensors, technology is rewriting the rules of production and consumption.
📌 Why This Matters: Through technology-innovation-in-textiles, brands gain agility, reduce environmental impact, and cater to evolving consumer expectations. Designers can push creative limits unbounded by material constraints, while consumers benefit from products that are healthier, more responsive, and inherently sustainable.